What is sodium alginate?
Sodium alginate is a sodium salt of alginic acid extracted from brown seaweed or kelp, and its molecules are composed of β-D-mannuronic acid (β-D-mannuronic, M) and α-L-gulo Uronic acid (α-L-guluronic, G) is formed by linking (1→4) bonds. The aqueous solution of sodium alginate has a high viscosity and has been used as a food thickener, stabilizer, emulsifier, etc. Sodium alginate is a non-toxic food additive, which was included in the United States Pharmacopoeia as early as 1938. Sodium alginate contains a large amount of -COO-, which can exhibit polyanion behavior in aqueous solution and has certain adhesion, and can be used as a drug carrier for treating mucosal tissues. Under acidic conditions, -COO- transforms into -COOH, the degree of ionization decreases, the hydrophilicity of sodium alginate decreases, and the molecular chain shrinks. When the pH value increases, the -COOH group dissociates continuously, and the hydrophilicity of sodium alginate decreases. Therefore, sodium alginate has obvious pH sensitivity. Sodium alginate can quickly form a gel under extremely mild conditions. When there are cations such as Ca2+ and Sr2+, the Na+ on the G unit undergoes an ion exchange reaction with the divalent cation, and the G units accumulate to form a cross-linked network structure, thereby forming Hydrogels. Sodium alginate forms a gel under mild conditions, which can avoid the inactivation of active substances such as sensitive drugs, proteins, cells and enzymes. Due to these excellent properties, sodium alginate has been widely used in the food industry and pharmaceutical fields.
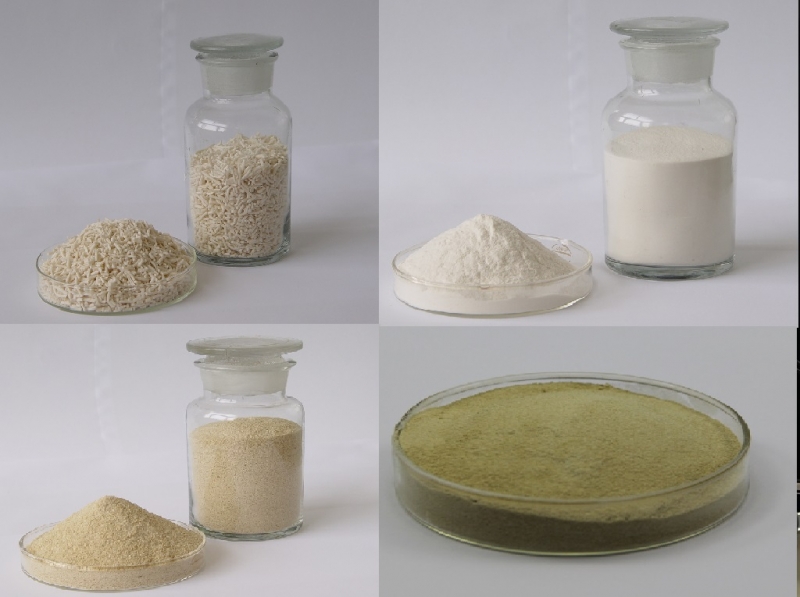
If devided by viscosity, sodium alginate can be devided into low viscosity sodium alginate (less than 150cps, 1% solution), medium vicosity sodium alginate (150-400cps, 1% solution), high viscosity sodium alginate (400-1200cps, 1% solution). If devided by gel strength, sodium alginate contains high gel strength sodium alginate, normal gel strength sodium alginate, low gel strength sodium alginate.

brown seaweed
Sodium alginate manufacturing process
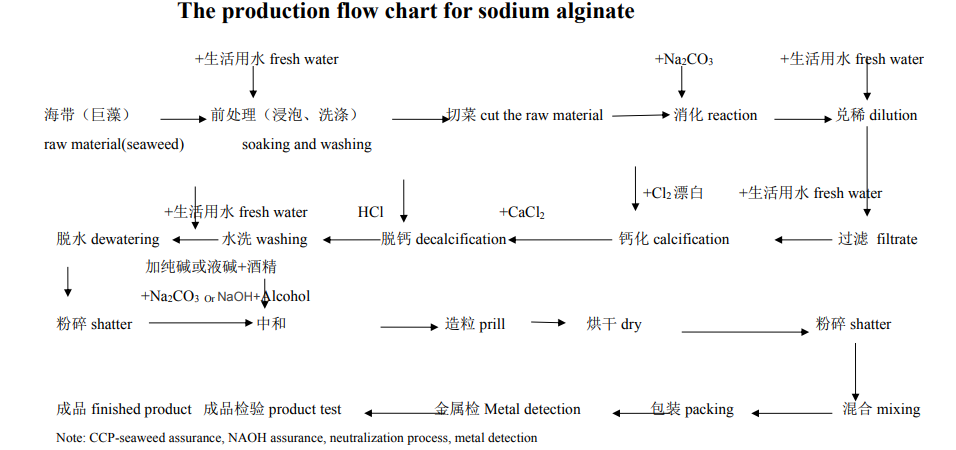
The technical process of sodium alginate is as follows: dry or wet seaweed (algae) is crushed, washed to remove impurities, extracted with strong alkaline water, and clarified to obtain a coarse alginate solution, which is precipitated by calcium chloride to obtain colored calcium alginate After decolorization and deodorization, it is treated with acid to remove soluble impurities to obtain alginic acid precipitation, and react with sodium carbonate or sodium hydroxide to obtain sodium alginate, and then dry, pulverize and sieve to obtain sodium alginate powder.
Physical and chemical properties
Sodium alginate is white or light yellow powder, almost odorless and tasteless. Sodium alginate is soluble in water, but insoluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, and chloroform. Soluble in water to become a viscous liquid, the pH value of 1% aqueous solution is 6-8. The viscosity is stable when the pH is 6-9, and the viscosity decreases when heated above 80°C. Sodium alginate is non-toxic, LD50>5000mg/kg. The chelating agent can complex the divalent ions in the system, so that sodium alginate can be stabilized in the system.
1. Composition
Molecular formula of sodium alginate: C6H7NaO6, mainly composed of sodium salt of alginic acid, composed of β-D-mannuronic acid (M unit) and α-L-guluronic acid (G unit) relying on β-1,4 - Copolymers linked by glycosidic bonds and composed of GM, MM and GG fragments in different proportions.
2. Molecular weight
The molecular weight of sodium alginate used in commercial products is usually dispersed like polysaccharides. Therefore, the molecular weight of one alginate usually represents the average value of all molecules of the group. The most common ways of expressing molecular weight are number average molecular weight (Mn) and weight average molecular weight (Mw).
In polydisperse molecular populations, usually Mw>Mn. The coefficient of Mw/Mn is the dispersibility index, and the typical index range of sodium alginate commodity is 1.5-2.5. The most commonly used methods for determining molecular weight are calculated based on intrinsic viscosity and light scattering measurements.
3. Molecular formula
The molecular formula is C6H9NaO7.
4. pH value
Sodium alginate is slightly soluble in water and insoluble in most organic solvents. It dissolves in alkaline solutions, making the solution viscous. Sodium alginate powder becomes wet with water, and the hydration of the particles makes the surface sticky. The particles then quickly bond together to form clumps, which are very slowly fully hydrated and dissolved. Sodium alginate is more difficult to dissolve in water if the water contains other compounds that compete with alginate for hydration. Sugar, starch or protein in the water will reduce the hydration rate of sodium alginate, and the mixing time must be extended. Salts of monovalent cations such as NaCl have similar effects at concentrations above 0.5%. The pH of sodium alginate in 1% distilled water is about 7.2.
5. Stability
Sodium alginate is hygroscopic, and the amount of water contained in equilibrium depends on the relative humidity. Dry sodium alginate is quite stable when stored at a temperature of 25°C or below in a well-sealed container. Sodium alginate solution is stable at pH 5-9. The degree of polymerization (DP) and molecular weight are directly related to the viscosity of sodium alginate solution, and the decrease in viscosity during storage can be used to estimate the degree of depolymerization of sodium alginate. Sodium alginate with a high degree of polymerization is less stable than sodium alginate with a low degree of polymerization. Sodium alginate has been reported to undergo proton-catalyzed hydrolysis, which is dependent on time, pH and temperature. Propylene glycol alginate solution is stable at room temperature and at pH 3 to 4; when the pH is less than 2 or greater than 6, the viscosity will decrease rapidly even at room temperature.
What is sodium alginate used for?
1. sodium alginate used in food
Food Grade Sodium Alginate is used as a stabilizer for ice cream instead of starch and gelatin. It can control the formation of ice crystals, improve the taste of ice cream, and stabilize mixed drinks such as sugar water ice cream, ice sherbet, and frozen milk. Many dairy products, such as refined cheese, whipped cream, dry cheese, etc., use the stabilizing effect of sodium alginate to prevent the stickiness of food and packaging. It can be used as a covering for dairy ornaments to keep it stable and prevent frosting and cracked.
Sodium alginate is used as a thickener for salad (a cold dish), pudding (a dessert), jam, tomato sauce and canned products to improve the stability of the product and reduce the leakage of liquid.
Adding sodium alginate in the production of dried noodles, vermicelli, and rice noodles can improve the cohesiveness of the product tissue, make it strong in tension, large in curvature, and reduce the rate of broken ends, especially for flour with low gluten content, the effect is more obvious. Adding sodium alginate to bread, pastry and other products can improve the uniformity and water-holding effect of the internal tissue of the product, and prolong the storage time. Adding it to frozen confectionary products can provide thermal fusion protective layer, improve flavor escape, and improve the performance of melting point.
Sodium alginate can be made into various gel foods, maintains a good colloidal shape, does not seep or shrink, and is suitable for frozen foods and artificial imitation foods. It can also be used to cover fruits, meat, poultry and aquatic products as a protective layer, without direct contact with air, and prolong storage time. It can also be used as a self-setting agent for bread icing, stuffing, dessert coating, canned food, etc. It can still maintain its original shape in high temperature, freezing and acidic medium. It can also be used instead of agar to make elastic, non-sticky, transparent crystal jellybeans.

2. sodium alginate used in pharmaceutical preparations
Sodium alginate has been included in the United States Pharmacopoeia as early as 1938. Alginic acid was included in the British Pharmacopoeia in 1963. Alginic acid is insoluble in water, but it will swell when placed in water. Therefore, traditionally, sodium alginate is used as a binder for tablets, while alginic acid is used as a disintegrant for immediate-release tablets. However, the effect of sodium alginate on tablet properties depends on the amount put into the formulation, and in some cases, sodium alginate can promote tablet disintegration. Sodium alginate can be added during the granulation process instead of adding it as a powder after granulation, which makes the production process easier. The resulting flakes are mechanically stronger than when starch is used.
Sodium alginate is also used in the production of suspensions, gels and concentrated emulsions based on fats and oils. Sodium alginate is used in some liquid medicines to increase viscosity and improve suspension of solids. Propylene glycol alginate improves emulsion stability.
3. sodium alginate used in textile
Sodium alginate is used as a reactive dye paste in the printing and dyeing industry, which is superior to grain starch and other pastes. The printed textiles have bright patterns, clear lines, high color yield, uniform color yield, good permeability and plasticity. Sodium alginate paste is the best slurry for modern printing and dyeing industry, and it has been widely used in the printing of various fabrics such as cotton, wool, silk, nylon, etc., especially for the preparation of dyeing printing paste.
Use sodium alginate and starch mixture or replace starch to prepare warp yarn size, which can not only save a lot of grains, but also make warp yarn fibers lint-free, friction-resistant, and end-break rate less, thereby improving weaving efficiency. Alginate is effective on both cotton and synthetic fibers.

4. sodium alginate used in the pharmaceutical industry
The PS-type gastrointestinal double-contrast barium sulfate preparation made of alginate sulfate dispersant has the characteristics of low viscosity, fine particle size, good wall adhesion and stable performance.
PSS is a kind of fucoidan diester sodium developed from alginic acid, which has the functions of anticoagulation, lowering blood fat and lowering blood viscosity.
Using sodium alginate instead of rubber and gypsum as dental impression material is not only cheap, easy to operate, but also prints more accurate tooth shapes.
Alginate can also be used to make various hemostatic agents, including hemostatic sponge, hemostatic gauze, hemostatic film, scald gauze, spray hemostatic agent, etc.